|
|
HSBC Climate Paris Aligned UCITS ETFs
Aligned with the world’s efforts to reverse climate change
The Paris Agreement: a unified commitment to tackle global warming
Set during the 21st Conference of the Parties (COP21) in December 2015, the Paris Agreement is an international accord to address climate change concerns, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and ultimately limit global temperature rises to 1.5°C by 2050.
Investors are becoming increasingly aware of the threat climate change poses to their long-term objectives, and are endeavouring to limit global warming in line with the Paris Agreement by ensuring portfolios achieve net zero emissions by 2050.
Our Global and Regional Equity Exposures – MSCI Climate Paris Aligned Indices
The MSCI Climate Paris Aligned Indices provide investors with a pathway to support the decarbonisation of the economy while being compatible with the Paris Agreement requirements. The indices incorporate the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and are designed to exceed the minimum requirements for the EU Paris Aligned Benchmark.
Objectives and constraints
Source: HSBC Asset Management, MSCI
1. Green revenue is defined as revenue from goods and services including alternative energy, energy efficiency, green building, pollution prevention and sustainable water.
2. Brown revenue is defined as the revenue generated from thermal coal extraction, unconventional and conventional oil and gas extraction, oil refining, thermal coal based power generation, liquid fuel based power generation or natural gas based power generation.
3. Climate Value-at-Risk (Climate VaR) is designed to provide a forward-looking and return-based valuation assessment to measure climate related risks and opportunities in an investment portfolio. The fully quantitative model offers deep insights into how climate change could affect company valuations.
Our Listed Real Estate Exposure – FTSE EPRA Nareit Developed Green EU PAB Index
 |
HSBC MSCI World Climate Paris Aligned UCITS ETF |
More information |
 |
HSBC MSCI USA Climate Paris Aligned UCITS ETF |
More information |
 |
HSBC MSCI Europe Climate Paris Aligned UCITS ETF |
More information |
 |
HSBC MSCI Japan Climate Paris Aligned UCITS ETF |
More information |
Engagement as HSBC Asset Management
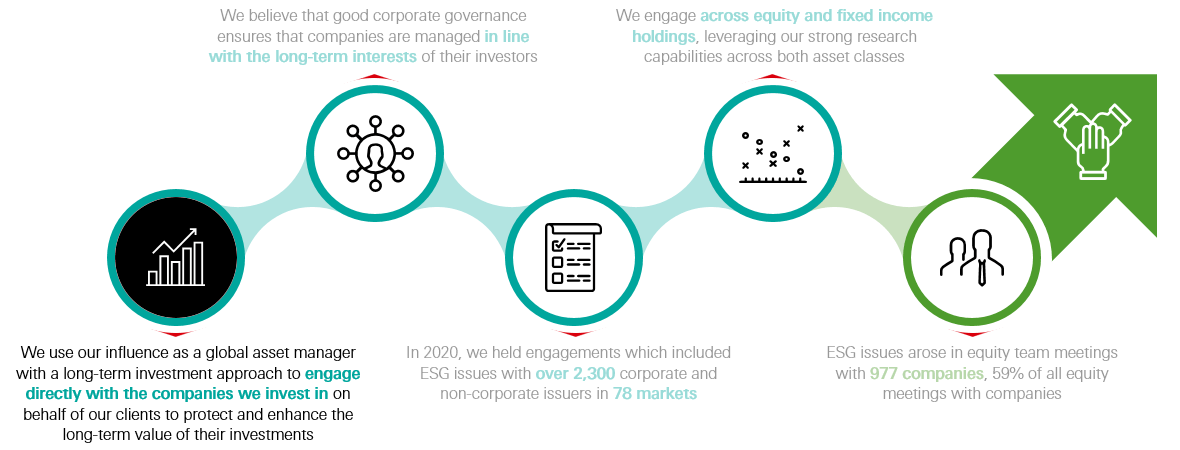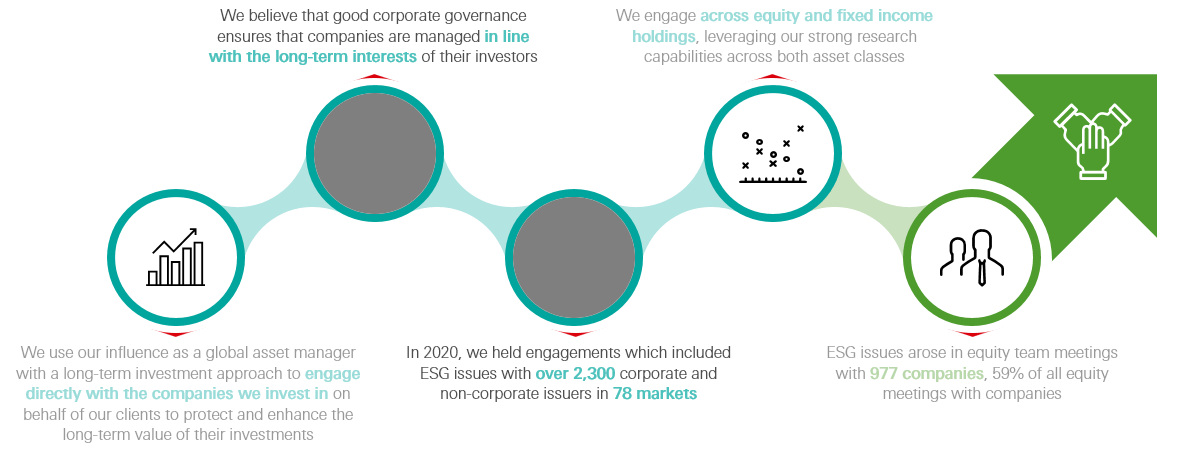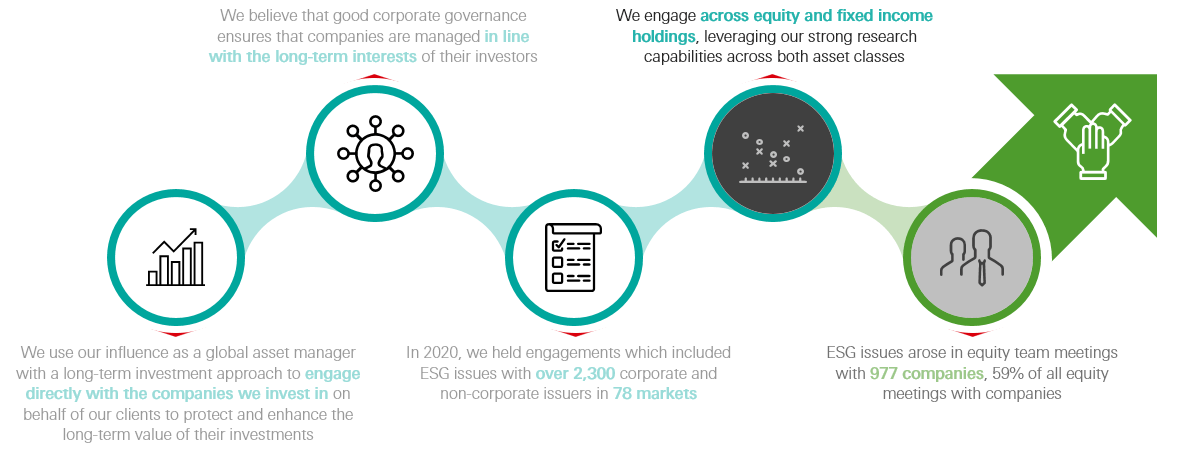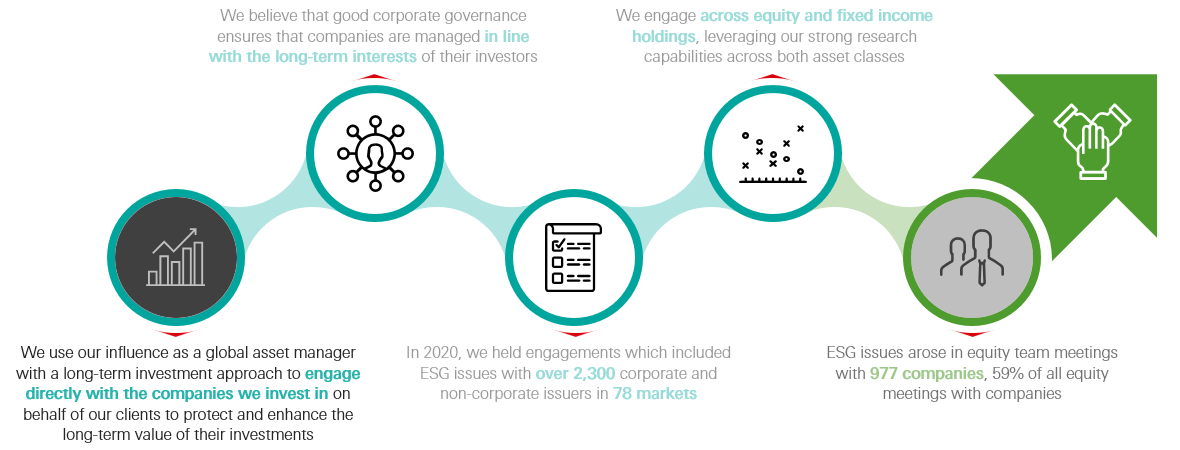
Source: HSBC Asset Management as at 31 December 2020.
-

Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)
Learn more about our ETFs -

Fund centre
View our ETF funds
Error message: There is an error with the ImagePromo component. Please check the log for more information
Key risks
- Counterparty Risk: The possibility that the counterparty to a transaction may be unwilling or unable to meet its obligations
- Derivatives Risk: Derivatives can behave unexpectedly. The pricing and volatility of many derivatives may diverge from strictly reflecting the pricing or volatility of their underlying reference(s), instrument or asset
- Exchange Rate Risk: Changes in currency exchange rates could reduce or increase investment gains or investment losses, in some cases significantly
- Index Tracking Risk: To the extent that the Fund seeks to replicate index performance by holding individual securities, there is no guarantee that its composition or performance will exactly match that of the target index at any given time (“tracking error”)
- Interest Rate Risk: When interest rates rise, bond values generally fall. This risk is generally greater the longer the maturity of a bond investment and the higher its credit quality
- Investment Leverage Risk: Investment Leverage occurs when the economic exposure is greater than the amount invested, such as when derivatives are used. A Fund that employs leverage may experience greater gains and/or losses due to the amplification effect from a movement in the price of the reference source
- Liquidity Risk: Liquidity Risk is the risk that a Fund may encounter difficulties meeting its obligations in respect of financial liabilities that are settled by delivering cash or other financial assets, thereby compromising existing or remaining investors
- Operational Risk: Operational risks may subject the Fund to errors affecting transactions, valuation, accounting, and financial reporting, among other things
Index-based Investing - The value of investments and any income from them can go down as well as up and investors may not get back the amount originally invested. Where overseas investments are held the rate of currency exchange may also cause the value of such investments to fluctuate. Investments in emerging markets are by their nature higher risk and potentially more volatile than those inherent in some established markets. Stock market investments should be viewed as a medium to long term investment and should be held for at least five years. Any performance information shown refers to the past and should not be seen as an indication of future returns.


